RELATED
MESSAGE
The Precision Time Protocol (PTP) has the following key features:
High-precision synchronization: It can achieve sub-microsecond or even higher-precision time synchronization, which can meet the extremely demanding application scenarios for time accuracy, such as aerospace and high-precision experiments in scientific research.
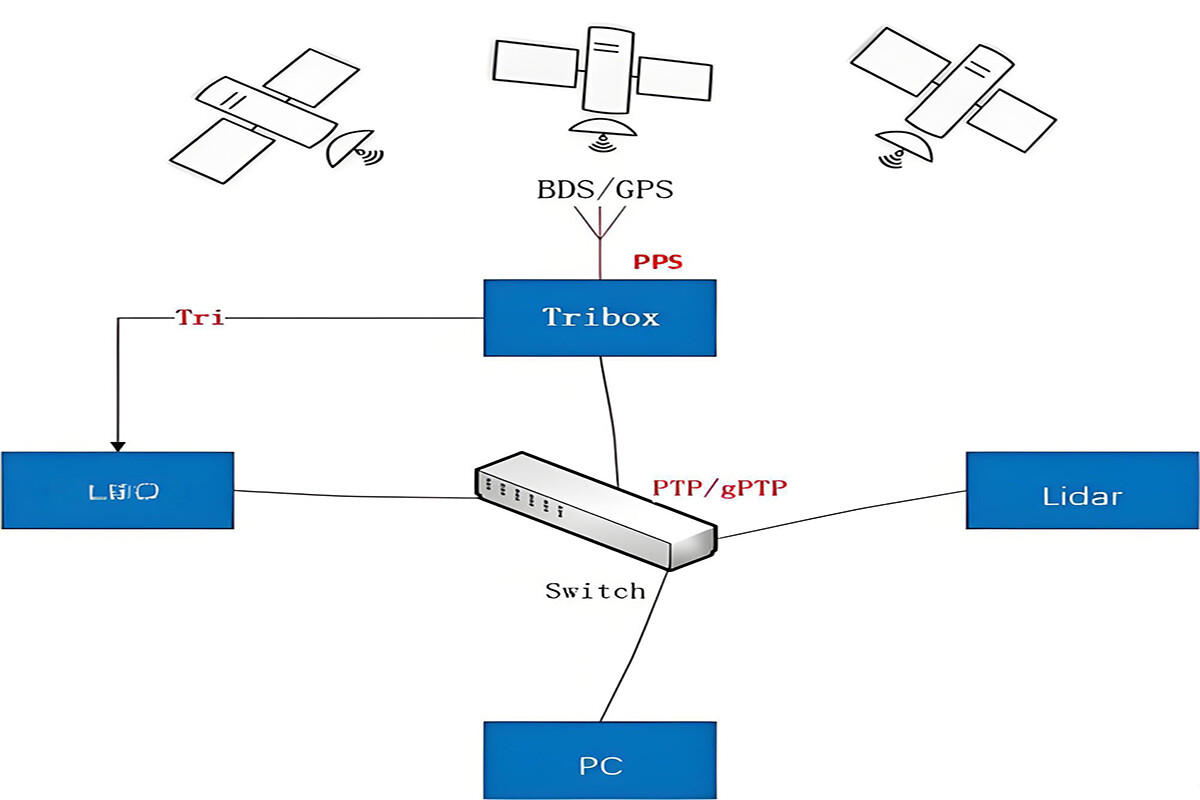
Master-slave clock architecture: Adopting a master-slave clock architecture, one master clock in the network serves as the time reference, and multiple slave clocks synchronize their time with the master clock to ensure that the time of devices throughout the network remains consistent.
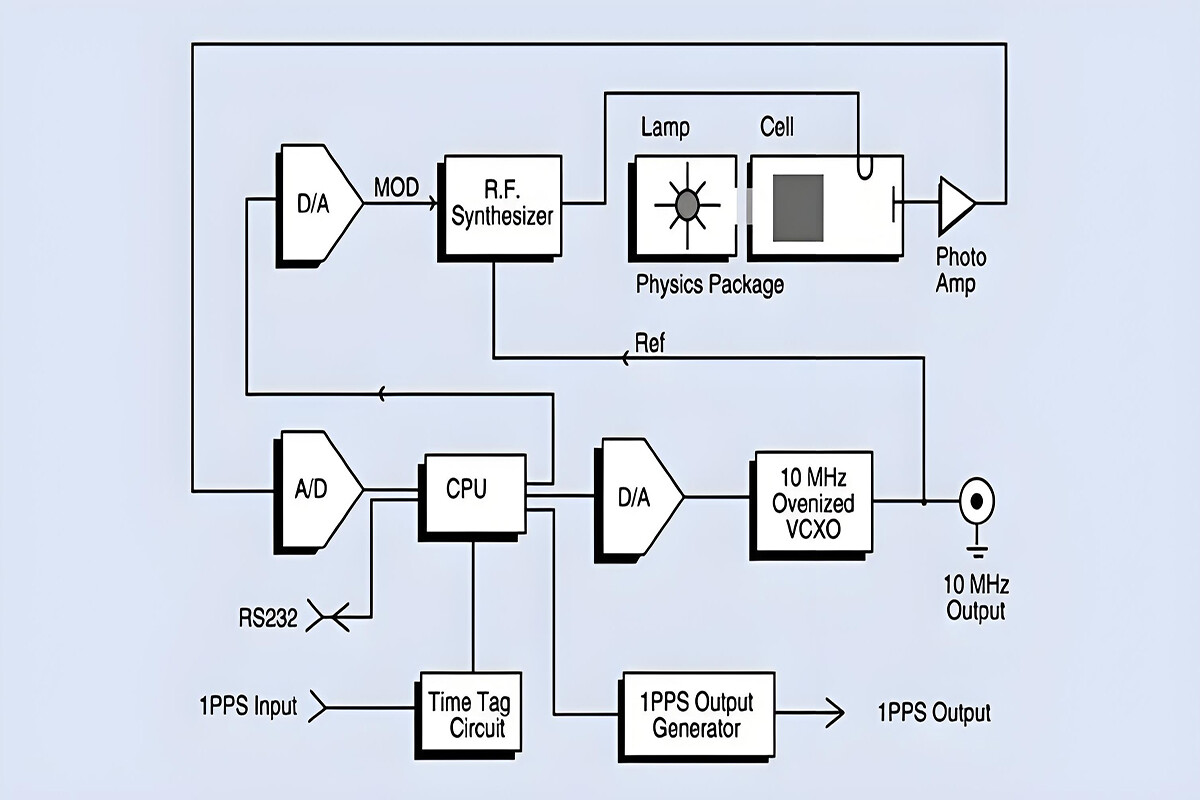
Timestamp mechanism: By adding timestamps to messages, it records the exact moments when messages are sent and received. Using these timestamp information, it calculates the message transmission delay and the time deviation between the master and slave clocks, thus achieving precise time synchronization.
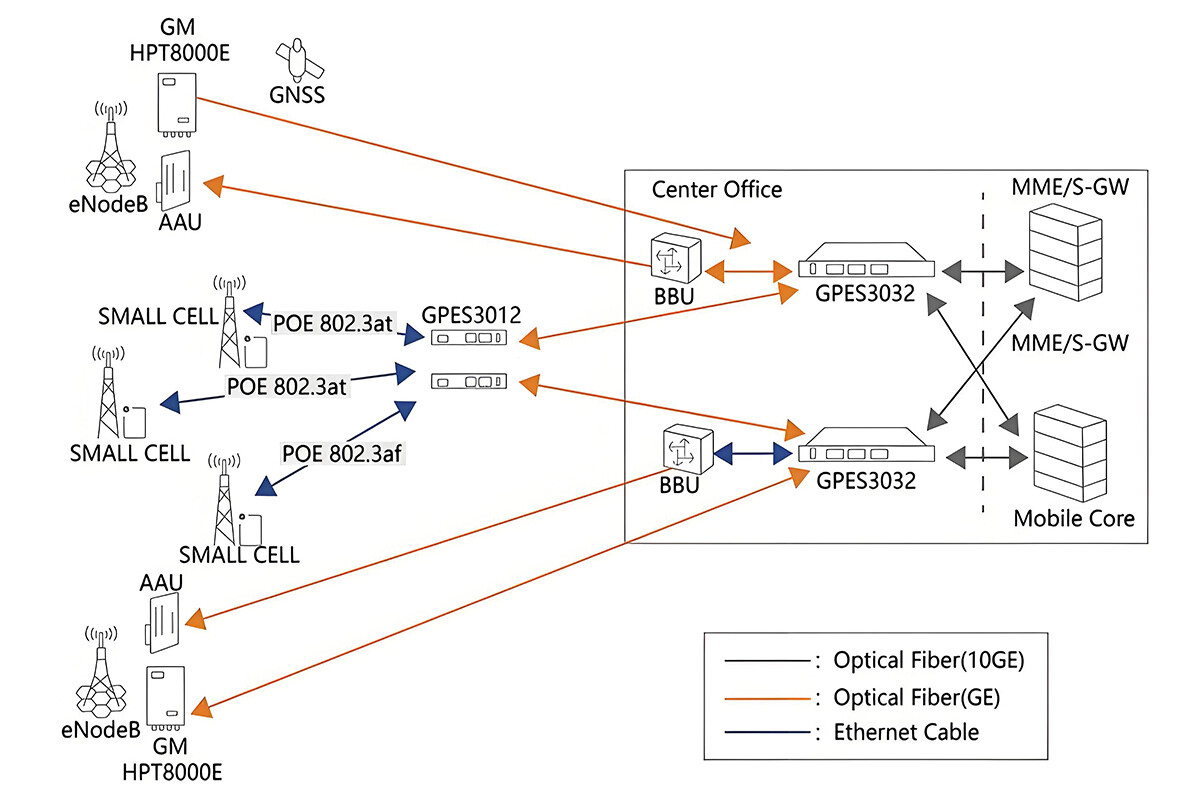
Support for multiple network topologies: It can adapt to various network topologies such as star, tree, and ring. Whether it is a simple small-scale network or a complex large-scale network, PTP can be used to achieve efficient time synchronization, showing strong flexibility and adaptability.
Automatic compensation for network delay: PTP can automatically measure the network transmission delay and compensate for it. Even in the presence of complex and changeable situations such as data congestion and link failures in the network, it can ensure the accuracy of time synchronization and reduce the impact of network conditions on time synchronization.
Transparency: PTP is usually transparent to upper-layer applications and devices in the network. It can be easily deployed and applied without major modifications to existing network devices and applications, reducing the implementation cost and difficulty.
Scalability: It is easy to be extended to large-scale networks. As the network scale expands and the number of devices increases, PTP can still maintain good performance. Through reasonable configuration of master-slave clocks and network parameters, it can meet the time synchronization requirements of networks of different scales.
Standardization: Based on the IEEE 1588 standard, it has unified specifications and definitions. As long as the devices from different manufacturers comply with this standard, they can achieve interoperability and seamless docking, which is beneficial for building complex network systems composed of devices from multiple manufacturers.
CONTACT US
Please use the form below to get in touch.
If you need a reply we will get in touch as soon as possible.